A role models a real-world job function or responsibility within LUSID. See how to create a role.
For example:
A data controller might require write access to all the data in LUSID.
A portfolio manager might require write access to certain portfolios.
A risk manager might require read-only access to all portfolios.
Each role has one or more policies, each of which grants (or denies) access to a particular feature or dataset. You can combine policies in any way you like to precisely model the professional duties of a role, and edit policies as these professional duties evolve over time.
You assign a role to one or more LUSID users. A user with that role inherits all the access rights granted by its policies. A user can have multiple roles. See how to assign policies, roles and users.
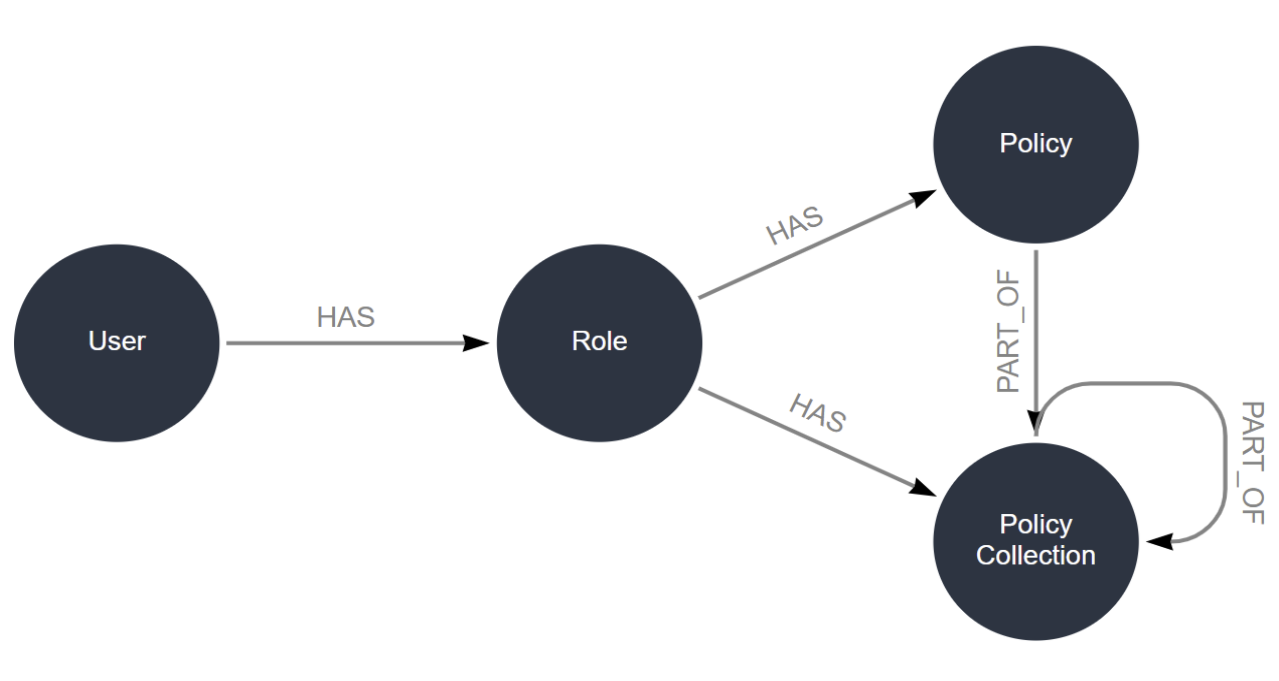
Note the following:
If a person changes job function (for example, a risk manager is promoted to data controller), you should assign the data controller role to that user rather than change the risk manager role to encompass their new responsibilities. Such a change would affect all other risk managers.
It’s possible for a user to inherit conflicting permissions from multiple roles. Each role therefore has a precedence, which determines which policies take effect. See how to set precedence.
A default set of roles is provided with LUSID for you to adopt or adapt.
